Programmes & Workshops
Local Food Security and Nutrition
The community will gain reliable access to fresh, nutrient-rich food harvested at peak ripeness—food that will be healthier than produce transported over long distances. This system will significantly reduce dependency on industrial food networks, external suppliers, and market fluctuations. By producing food locally, residents will enjoy greater control over quality, availability, and affordability, ensuring year-round nourishment for all families.


Environmental Sustainability
Small-scale farms will adopt sustainable, agroecological practices such as crop rotation, natural pest control, mulching, and composting. These methods will enrich the soil, restore biodiversity, and minimise the need for synthetic fertilisers and pesticides. By drastically reducing food miles, plastic packaging, and cold-chain logistics, the community’s carbon footprint will decrease substantially. Support long-term climate resilience and ecological balance. Diversified farming systems—featuring a mix of crops, herbs, fruits, and small livestock—will offer superior resilience against climate changes, pests, and diseases. This diversity will ensure a more stable and reliable food supply, even in times of environmental or economic uncertainty.
Economic and Social Cohesion
Small farms will create local employment opportunities, keeping economic value circulating within the community. These farming areas will become vibrant social hubs where residents gather for farm stands, weekend markets, workshops, and shared workdays. Such activities will foster social interaction, deepen community bonds, and strengthen inter-generational relationships. As a result, the farming subdivision will help build a united, cooperative, and economically empowered community.

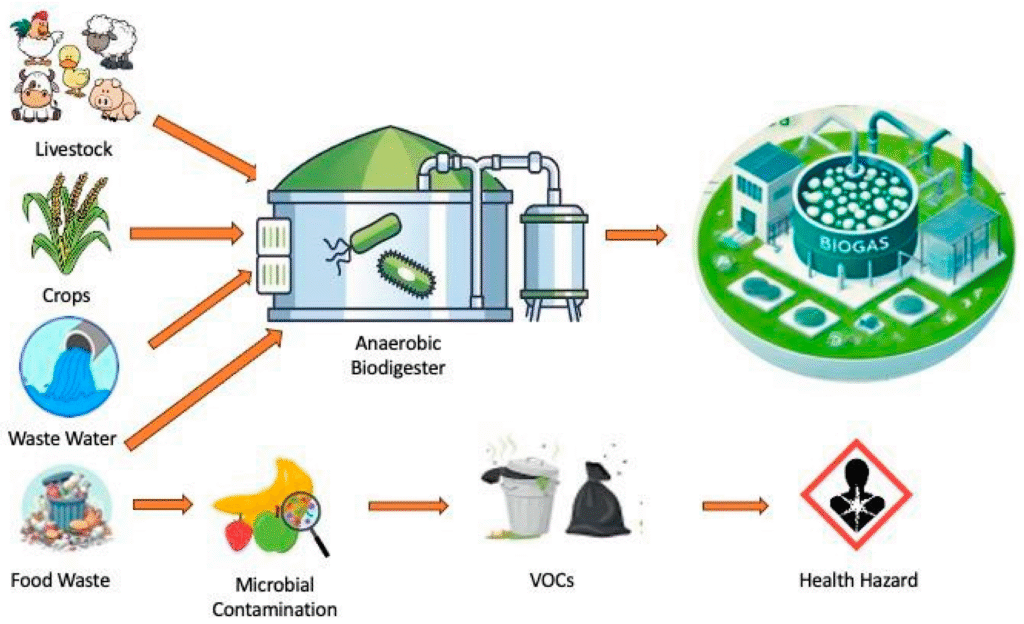
Zero-Waste and Space-Saving Agricultural Systems
Organic materials—such as crop residues, food scraps, and animal manure—will not be discarded, but instead will be repurposed into nutrient-rich inputs for the farming ecosystem. Composting and Manure Use. Organic waste will be channelled into anaerobic digesters to produce biogas, a clean and renewable energy source for cooking or electricity generation. The remaining digestate will be used as an organic fertiliser. Innovative space saving farming techniques that will allow for increased production even in limited spaces such as Vertical farming, Aquaponics, Raised-bed intensive gardening for high-yield crops in compact areas
Farming Programmes and Workshops
The community will gain reliable access to fresh, nutrient-rich food harvested at peak ripeness—food that will be healthier than produce transported over long distances. This system will significantly reduce dependency on industrial food networks, external suppliers, and market fluctuations. By producing food locally, residents will enjoy greater control over quality, availability, and affordability, ensuring year-round nourishment for all families.


Skill Development
Through participation, children will develop important life skills such as responsibility, patience, teamwork, observation, and problem-solving. These experiences will instil a sense of purpose and connection to the land.
Advanced training programmes—such as a “Future Farmer Initiative”—will support youths interested in pursuing careers in regenerative and sustainable agriculture. These programmes will ensure that agricultural knowledge is preserved, expanded, and passed thoughtfully to the next generation.

OHA!
